DISCO: Disentangled Image Colorization via Global Anchors
Abstract
Colorization is multimodal by nature and challenges existing frameworks to achieve colorful and structurally consistent results. Even the sophisticated autoregressive model struggles to maintain long-distance color consistency due to the fragility of sequential dependence. To overcome this challenge, we propose a novel colorization framework that disentangles color multimodality and structure consistency through global color anchors, so that both aspects could be learned effectively. Our key insight is that several carefully located anchors could approximately represent the color distribution of an image, and conditioned on the anchor colors, we can predict the image color in a deterministic manner by utilizing internal correlation. To this end, we construct a colorization model with dual branches, where the color modeler predicts the color distribution for anchor color representation, and the color generator predicts the pixel colors by referring the sampled anchor colors. Importantly, the anchors are located under two principles: color independence and global coverage, which is realized with clustering analysis on the deep color features. To simplify the computation, we creatively adopt soft superpixel segmentation to reduce the image primitives, which still nicely reserves the reversibility to pixel-wise representation. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves notable superiority over various mainstream frameworks in perceptual quality. Thanks to anchor-based color representation, our model has the flexibility to support diverse and controllable colorization as well.
Method
Given a grayscale input G, we extract the feature map F and the local affinity association map A at feature extraction stage. Then, the tokenized backbone feature F′ is used for anchor-based color modeling and anchor-guided color generation respectively. Particularly, the anchors are adaptively located by the anchor locator. At last, by pixel-level refinement, we obtain the color output C. ⊙ denotes Hadamard product and ⊕ denotes concatenation along the channel axis.
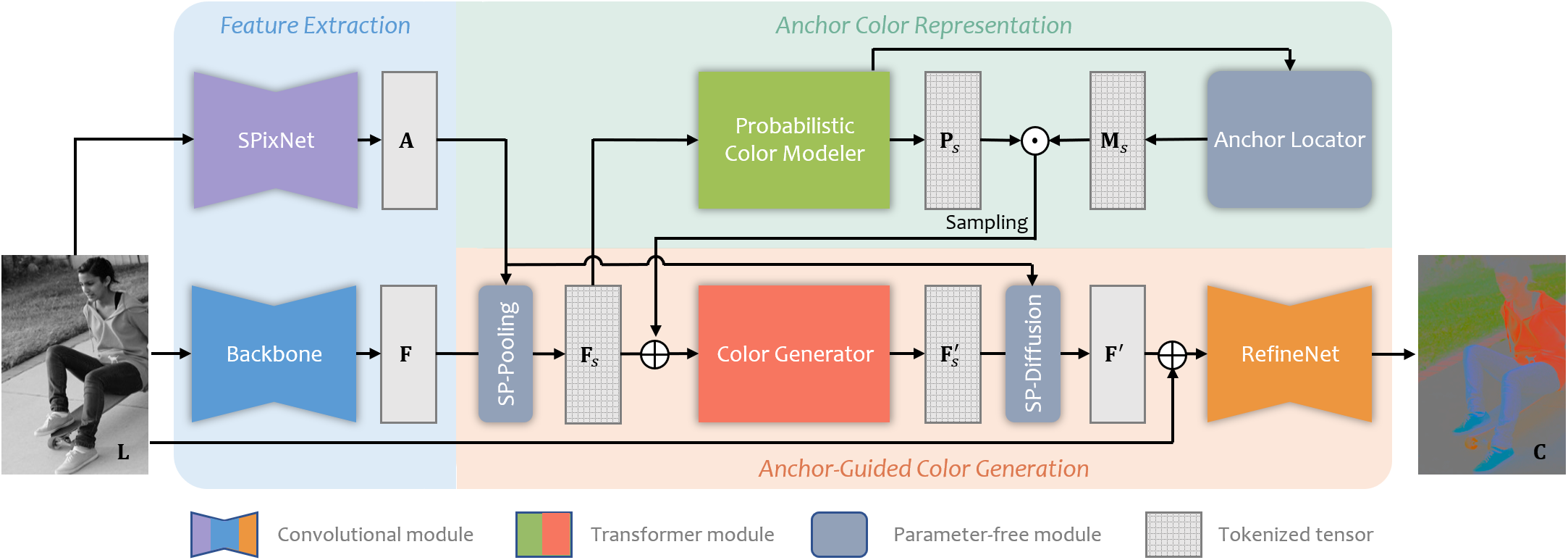
Model overview
Results
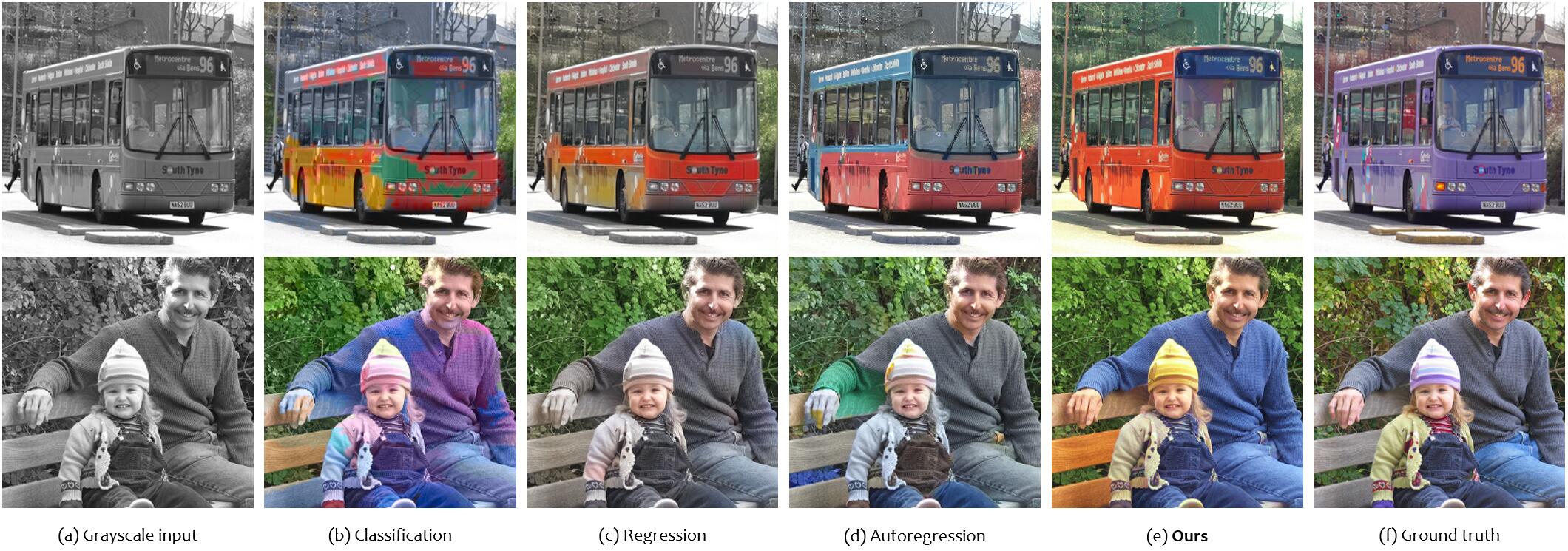
Comparing to natural scenes that usually have little color ambiguity, man-made scenes, such as human clothes, vehicles, sport facilities, and daily articles, may present diverse colors potentially and thus are more challenging to colorization algorithms. Here we mainly illustrate results on such scenes in comparison with existing colorization methods:CIColor, ChromaGAN, UGColor, InstColor, Deoldify, ColTran, for which we use their official implementation and pretrained models for comparison.
For inference, the input grayscale image is first resized to 256x256 before fed to the model and the output chromatic channels are bilinearly rescaled to the orginal resolution, which together makes the colorized RGB image. Below illustrates a subset of our comparative cases.
| Input | UGColor | InstColor | Deoldify | ColTran | Ours | Ground truth |

Materials
Full set of case comparison: GoogleDrive | OneDrive
Our results on dataset: COCO5k | ImageNet10k
Evaluation metrics: Python Implementation
Citation
If you find our dataset and paper useful for your research, please consider citing our work:
@article{XiaHWW22,
author = {Menghan Xia and Wenbo Hu and Tien-Tsin Wong and Jue Wang},
title = {Disentangled Image Colorization via Global Anchors},
journal = {ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG)},
volume = {41},
number = {6},
pages = {204:1--204:13},
year = {2022}
}


